8 Market Research Strategies used by Marketing Professionals
If you read our tutorial on how to conduct market research, you are already on your way to finding a […]
Read More »Become a successful marketing consultant: Learn more
If you are in the restaurant industry, or plan to be, you have found the right article.
Today, we are going to review the most important financial ratios for the restaurant industry.
Restaurant industry financial ratios:
The most important restaurant industry financial ratios are:
1. COGS as a percentage of sales revenue
2. Gross margin
3. Total payroll as a ratio
4. Operating expenses as a ratio
5. Profit margin
Financial ratios in the restaurant business are very important to regularly manage and monitor. All these ratios are highly dependent on sales revenue, so having your restaurant marketing systems ramped up is absolutely core to being able to have healthy financial ratios.
Go here for an excellent article on building your restaurant marketing strategy:
What is the best marketing strategy for restaurants? (Awesome plan)
With that, let's now get into the restaurant financial ratios.
Measuring cost of goods sold (COGS) is an important factor in the food industry as it helps businesses understand their profitability and determine their pricing.
In a general sense for most restaurants, COGS represents all the food costs that were used to serve a paying customer.
That is, a restaurant buys food and beverages from a supplier, and after additional operating costs, resells this food to the customer.
Tracking COGS helps a food business stay on top of their food expenses and monitor their spending on food for any potential cost savings.
Here is an example of a real restaurant we work with who has 18 locations.
This is one of their stores:
Notice that the COGS as a percentage of sales revenue is extremely important for at least two reasons:
By tracking the cost of goods sold, restaurants can better understand their profitability and determine the pricing that will be necessary to remain competitive in the market.
They can also use the data to create cost effective solutions to maximize their profits. Additionally, measuring COGS allows businesses to stay on top of their expenses. By understanding the cost of production, businesses can identify areas of potential cost savings and make adjustments to their operations accordingly. For example, if the cost of certain ingredients is too high, businesses can look for cheaper alternatives or switch to a different supplier.
This can help businesses save money and increase their profits.
Finally, measuring COGS can help businesses understand the impact of their pricing decisions. By understanding the cost of production, businesses can determine whether a certain price is too high or too low.
For an excellent article about the financial metrics of some of the biggest food suppliers in the U.S., go here:
Food manufacturing financial ratios (Hormel vs Pepsi vs Nestle)
Additionally, if you need help in developing your marketing strategy to increase your restaurant sales, here is a very helpful article:
Top 3 Forms of Advertising Marketing That a Food Business Should Use
Gross profit is an important measure of success in the food industry, as it helps businesses to effectively track their progress and understand their financial performance.
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from total revenue.
This metric helps companies identify the total profit from their product sales, as well as their overall production costs.
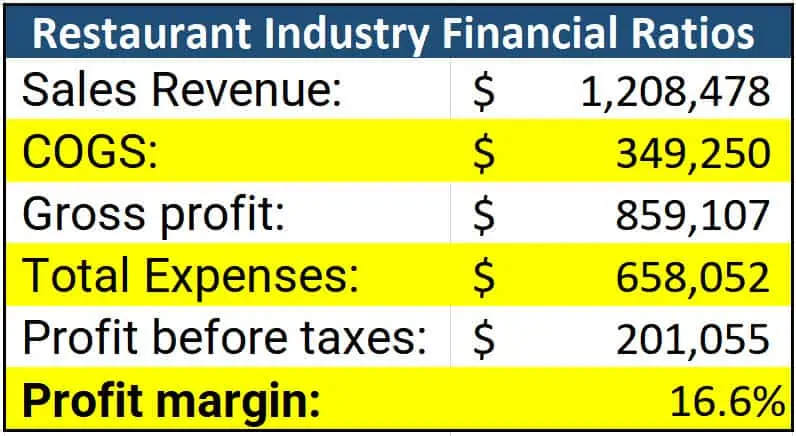
Here’s an example, using our restaurant from above:
Here’s how these number are calculated:
$1,208,478 (Sales revenue) - $349,250 (COGS) = $859,228 (Gross profit)
Gross profit / sales revenue = Gross margin
$859,2287 / $1,208,478 = 71.1%
By tracking their gross profit, food industry businesses can strategize and make adjustments to improve their financial performance. Businesses can also use gross profit to set prices, understand their customer base, and evaluate their operations.
For example, if a restaurant notices that their gross profit is dropping, they can use this metric to identify areas that need improvement. This may include evaluating their product mix or labor costs, or finding ways to increase customer loyalty.
Gross profit also helps businesses to identify their most profitable products and operations.
For example, a restaurant may find that one of their dishes is more profitable than the others and they can use this insight to create more of that dish or tailor their menu accordingly.
Monitoring gross profit can also help businesses understand the impact of any changes that they make inside or outside of their business, such as new recipes or marketing strategies.
Overall, tracking gross profit is essential for businesses in the food industry as it provides valuable insight into their financial performance and helps them make informed decisions about their operations.
Another reason why gross margin is such an important ratio to track in the restaurant industry, is because gross profit pays for your fixed expenses. And the lower you can keep your fixed expenses, the more profit margin you will have.
Here is an excellent article on how you can review some of the best food companies and apply some marketing lessons:
Marketing lessons from the most popular food companies (Top 10 brands)
Measuring payroll and payroll expenses is an important part of the financial management of a restaurant.
Payroll is typically one of the largest expenses, if not the largest expense, for a restaurant. Accurately measuring payroll can help a restaurant stay within its budget. Measuring payroll and payroll expenses helps the restaurant track how much money is being spent on labor costs and allows the restaurant to make informed decisions regarding staffing levels. It also assists in the calculation of payroll taxes and other payroll-related costs.
Here is an example of our restaurant:
Additionally, measuring payroll expenses helps the restaurant identify areas where it may be able to reduce costs. For instance, if a restaurant finds that they are spending too much on payroll, they may be able to identify ways to reduce labor costs by streamlining processes or reducing the number of employees.
This can help the restaurant maximize its profits and remain competitive in the industry.
Finally, measuring payroll expenses is important for understanding the financial health of the restaurant. By tracking payroll expenses, the restaurant can better understand its overall financial situation and can make adjustments as needed. This helps the restaurant remain financially sound and competitive in the restaurant industry.
Measuring operating expenses is important in the restaurant industry because it enables owners to have a better understanding of their business' financial health.
Knowing the amount of money spent on supplies, payroll, rent, and other expenses allows restaurant owners to make informed decisions about their operations.
Additionally, tracking operating expenses provides restaurant owners with important data that can help them make adjustments to their budget and operations.
For example, if a restaurant notices a sudden increase in the amount of money spent on supplies, the owner can analyze the cause and make changes to reduce costs.
Here's an example of your restaurant:
This helps them remain competitive and increase profits. Finally, tracking operating expenses is important for tax purposes. Having a clear understanding of all business expenses helps restaurant owners accurately report their finances to the IRS and remain in compliance with tax laws.
By keeping accurate records of their expenses, restaurant owners can reduce the risk of being audited. Overall, measuring operating expenses is essential in the restaurant industry as it helps owners make informed decisions, become more efficient, and remain compliant with federal, state and local laws.
Measuring profit before taxes is important in the restaurant industry because it allows restaurant owners to accurately assess the financial performance of their business.
By measuring profit before taxes, restaurateurs can determine the amount of money generated through sales and operations and can compare this amount to other businesses in the industry.
Here’s an example from our restaurant:
This helps them to identify areas where they can improve their operations and increase their profits. It also gives them an indication of how much money they will have to pay in taxes, which helps them plan their finances accordingly.
Furthermore, measuring profit before taxes also helps restaurateurs identify areas of potential cost savings, enabling them to make more informed decisions when it comes to their business strategies.
Ultimately, measuring profit before taxes helps restaurateurs to better understand the financial state of their business and make more informed decisions that will lead to greater profitability.
For an excellent list of articles that can help you build your restaurant marketing department, go here: