How to Conduct Market Research for your Business Idea
This short tutorial will help you cut right to the core of finding your best customers; the ones that […]
Read More »Become a successful marketing consultant: Learn more
If you’ve ever wondered what globalization is in simple words, you are at the right place.
That’s because we are going to review the definition of globalization and provide some answers as to why globalization is an important theory for trading among nations.
What is Globalization in Simple Words?
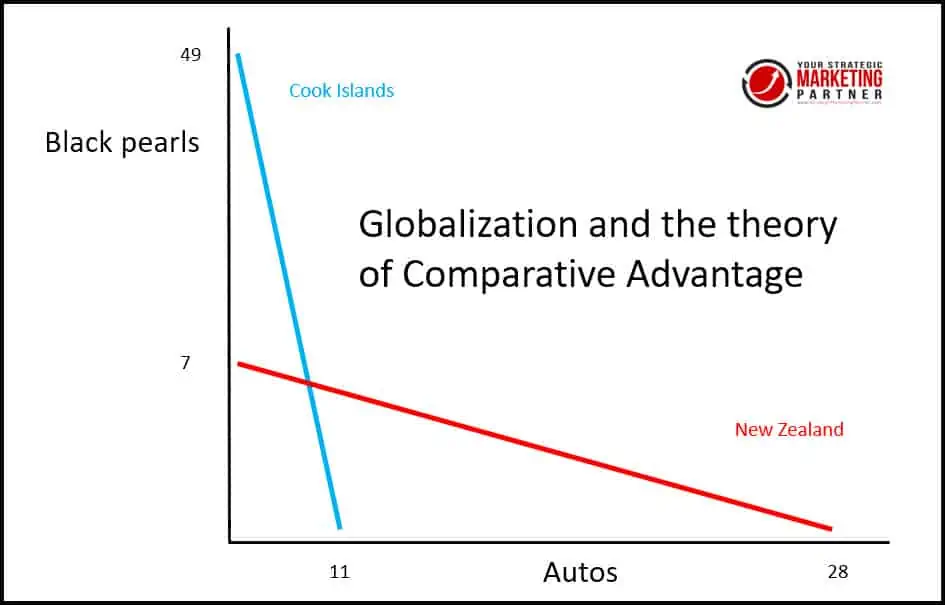
Globalization is the theory of comparative advantage among countries. This means that countries who are good at producing particular products or services should sell (export) to other countries that cannot produce the same product or service as efficiently. The main assumption is that not all nations produce all goods efficiently and will benefit from trading with one another.
Globalization essentially involves integrating a country’s economy with the global economy, in order to create more trading partners.
Through globalization, businesses and organizations operate on international scales.
Over time, it is said that globalization may significantly influence individual standards of living globally. This includes the availability of material goods, comfort, and an increase in wealth equality around the world.
Let’s now dig into globalization and how you can benefit from international business and marketing.
A globalized economy refers to an economy where there’s a free flow of products, technology, jobs, and information beyond national borders.
Economically, globalization describes the interdependence of countries and nations worldwide achieved by free trade.
Globalization is a cultural, social, legal, and political act in the following ways:
Globalization is based on the theoretical concepts of comparative advantage. According to the theory, countries that excel in producing particular goods or services should export to less efficient or experienced countries.
Conversely, the importing countries should export what they can produce best to the former countries. The theory’s underlying assumption is that not all nations produce all types of goods efficiently and will benefit from trading with one another.
Cultures have currently spread out beyond the confines of initial political boundaries. For instance, Greek culture has spread throughout Asia, Africa, Europe, and other countries. Satellite televisions also help in spreading cultures. TV shows of different countries are broadcasted in other countries around the world.
Established organizations currently operate on a global scale by running satellite branches and offices in multiple locations. For instance, KPMG operates offices worldwide, with its headquarters in Switzerland. Global companies also outsource tasks to professionals in different countries.
Similarly, any shirt sold in the US is possibly made using Chinese cotton by Thai workers and shipped by a French freighter operated by an Italian crew. Due to globalization, the production of a single product might involve workers from different countries.
Globalization and cooperation among various countries have led to tremendous growth in automotive exports. For instance, the big three automotive manufacturers in the USA, Ford, GM, and Chrysler, have expanded their car manufacturing business to Mexico. Due to the low cost of production in Mexico, these companies prefer manufacturing their cars in Mexico and shipping them back to the U.S.
Globalization also influences the food industry, technology, and the banking sector.
Globalization affects businesses in the following ways:
Increased competition is the most significant effect of globalization in the business environment. Competition is related to product/service costs or price, technological adaptation, target market, and production times. Companies that can produce goods and offer services quickly or sell cheaply automatically increases their market share.
Globalization offers manufacturers and consumers a large market and affects consumer behavior. Customers prefer companies that provide high-quality goods and services quickly, efficiently, and at low costs. Companies should be ready and flexible to price changes and customer preferences.
Information or knowledge is a valuable factor in production. Globalization facilitates information exchange or transfer among countries. Companies should always be on the lookout for information that can benefit their processes to adapt to global change. The constantly changing customer behavior and markets call for the swift transfer of information and knowledge across borders.
Another striking effect of globalization in business is the use of technology by internationally oriented companies to explore and exploit new businesses. The internet and eCommerce environment has made it possible for small and medium-sized enterprises to expand into international markets.
Technology is an important determiner of the quality of goods/services and competition. Companies leverage the latest technologies to increase product quality and customer satisfaction. Globalization also fosters the rate of technology transfer and improvements. Customer demands and expectations direct markets and most companies operating in capital-intensive markets should use modern technology to meet customer expectations.
While all businesses want to generate revenue and earn as much profits as possible, globalization significantly affects the prices of goods and services. Initially, the local competition was less intense, and companies offered products and services at high prices with minimal external pressure. However, globalization has changed these dynamics.
Globalization has the following effects on the price of goods and services:
Depending on the industry or business niche, businesses enjoy greater profitability through globalization. However, the price effects of globalization vary from one business to another, making it impossible to give an exact verdict on how specific businesses are affected.
Globalization also has an important effect on business tariffs. Global companies and agencies interact with international vendors and customers. Historically, countries used tariffs to protect their local businesses and punish rivals. However, with globalization taking full effect, there has been limited use of tariffs because:
As a result, most countries, businesses, and goods are not subjected to tariffs. This lowers the cost of goods and eases entry into new markets, which benefits small and medium-sized businesses. SMEs can compete effectively with larger entities that would otherwise be ahead of them in the market, suppose tariffs were imposed.
Initially, business costs and regulatory issues were major barriers to businesses and organizations going global. However, the increased adaptation of financial exchanges and trade developments has made globalization an economic phenomenon. Globalization has made people from different countries citizens of the world. The source of goods is becoming a secondary factor, and geographical distance isn’t a barrier anymore.